a) Chứng minh rằng \({\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1\,\,({0^0} \le x \le {180^0}).\)
b) Tìm \(\sin x\) khi \(\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{3}.\)
c) Tìm \(\cos x\) khi \(\sin x=0,3.\)
c) Tìm \(\cos x\) và \(\sin x\) khi \(\sin x - \cos x = \dfrac{2}{3}.\)
Giải
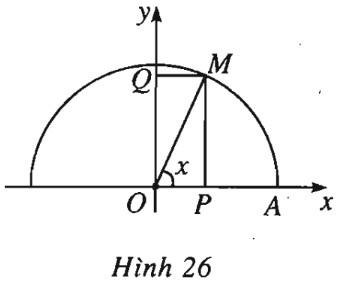
(h.26).
Advertisements (Quảng cáo)
a) \(\sin x = \overline {OQ}, \cos x = \overline {OP},\)
\({\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = O{Q^2} + O{P^2} = 1.\)
b) \(\sin x = \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}x} = \dfrac{{2\sqrt 2 }}{3}.\)
c) \(\cos x = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\sin }^2}x} = \pm \sqrt {0,91} .\)
d) Giải hệ \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\sin x - \cos x = \dfrac{2}{3}\\{\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1\end{array} \right.\)
Ta có \(\sin x = \dfrac{{\sqrt {14} + 2}}{6}, \cos x = \dfrac{{\sqrt {14} - 2}}{6}.\)
